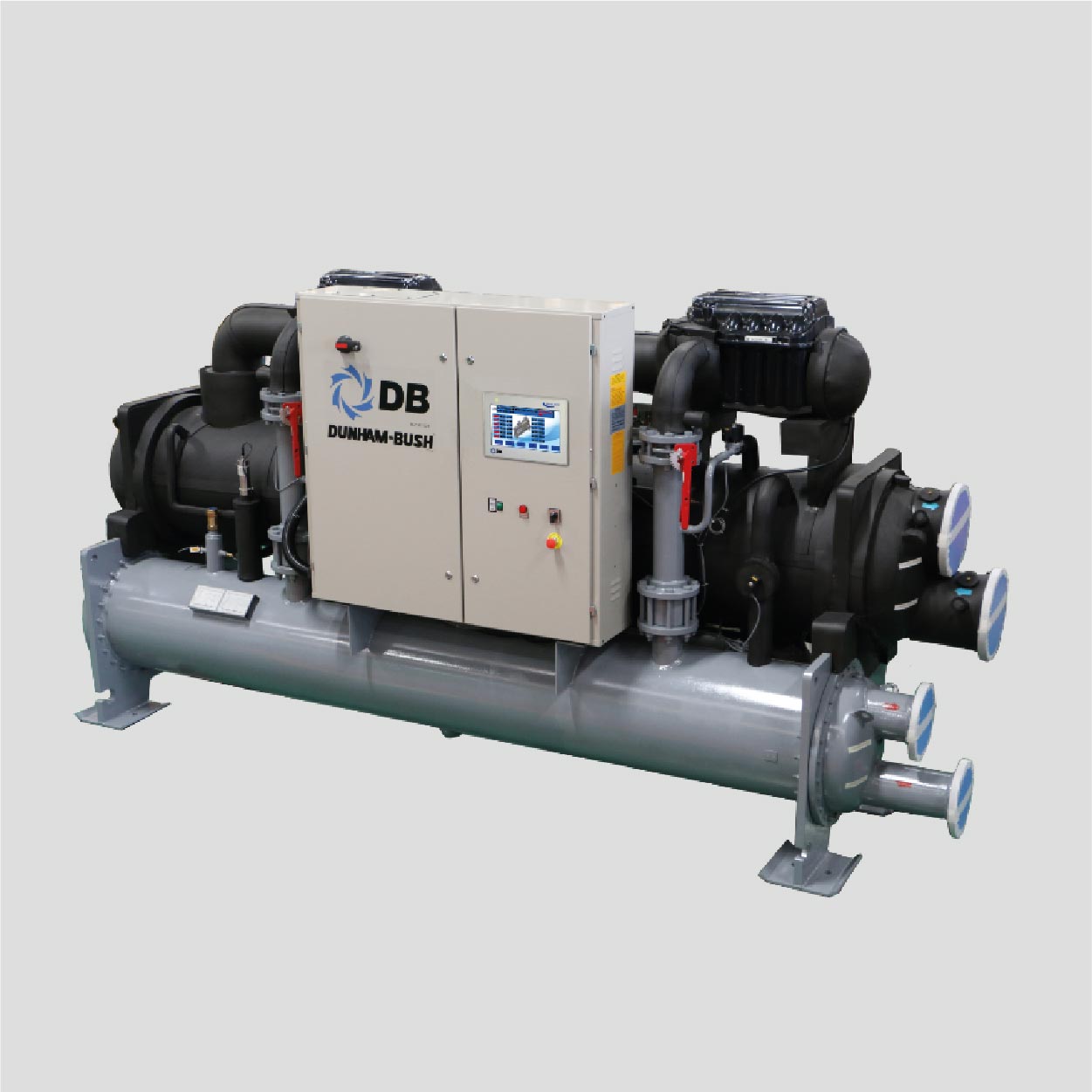
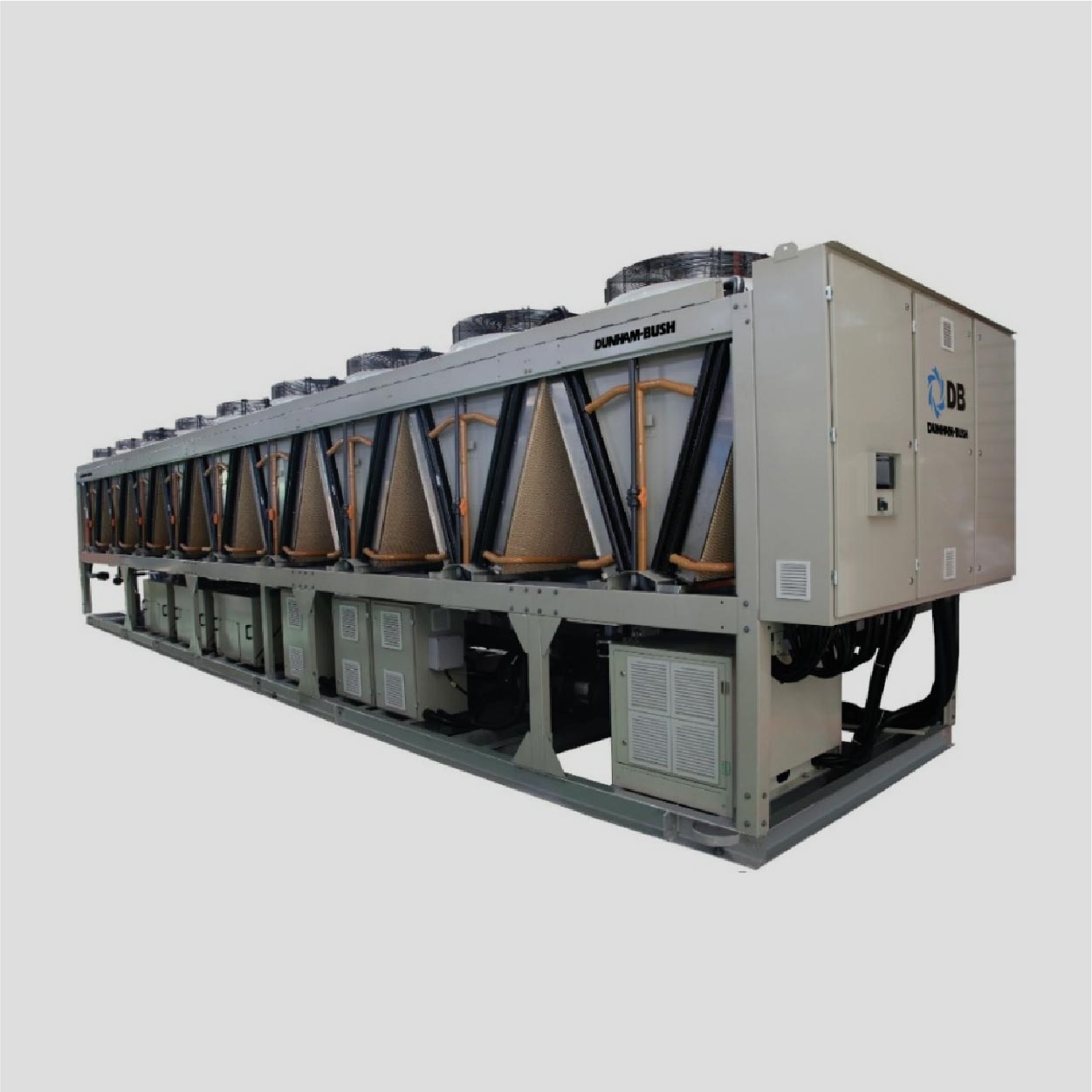
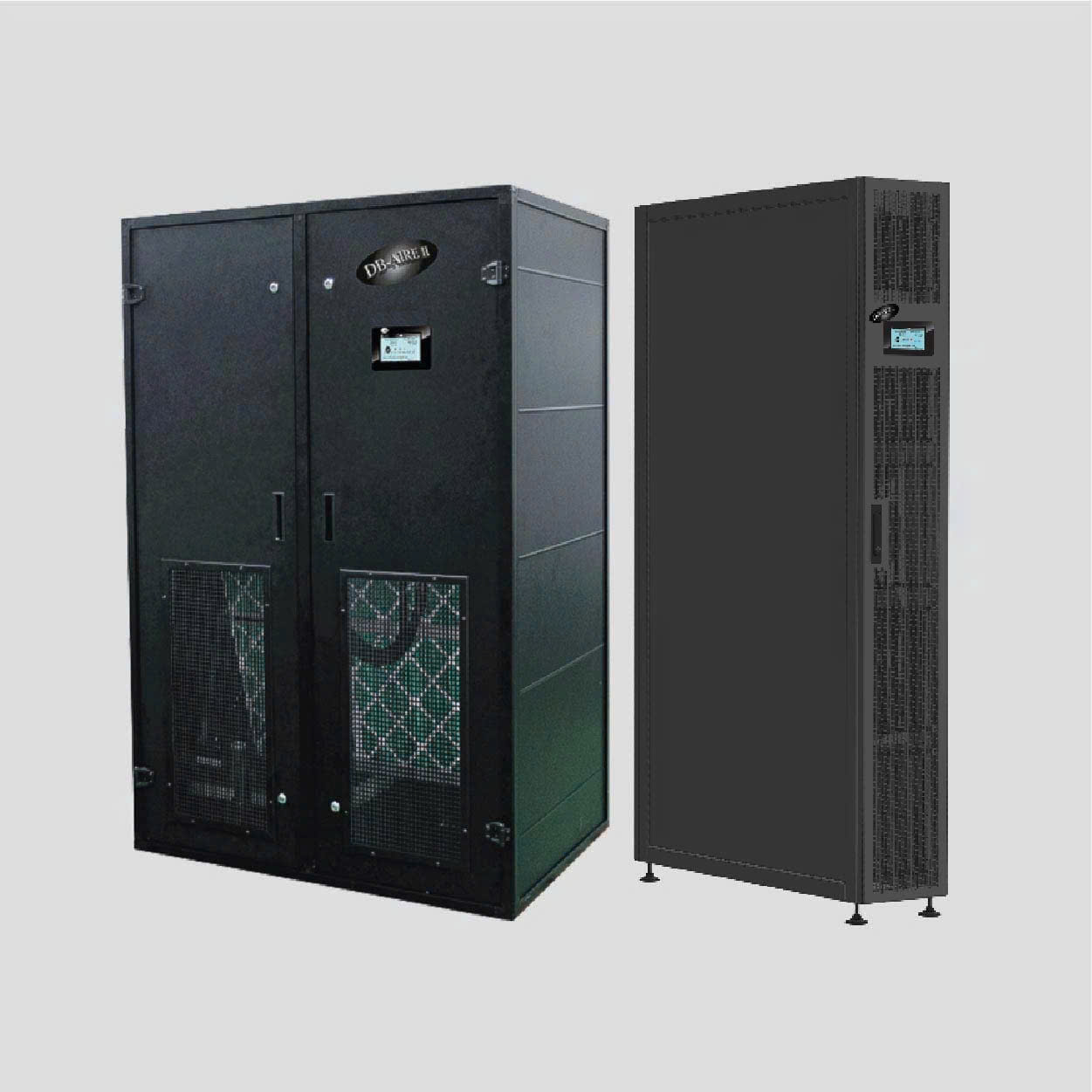
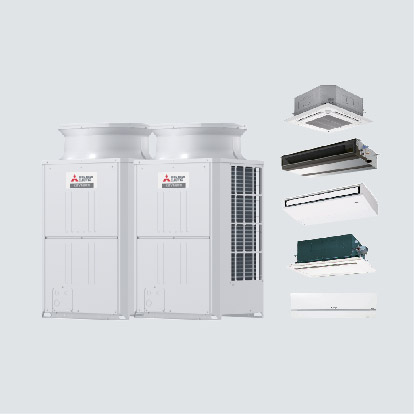
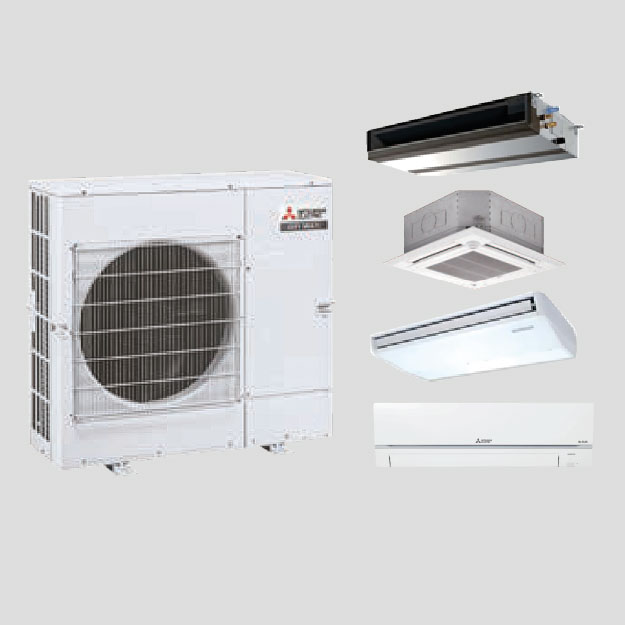
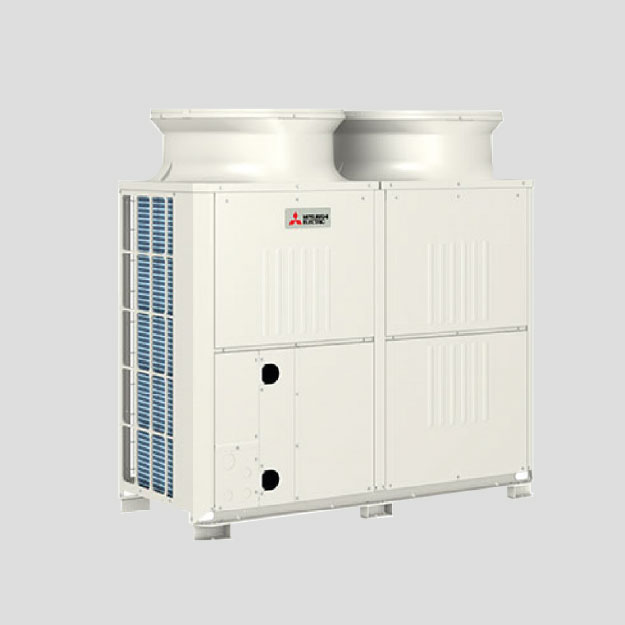
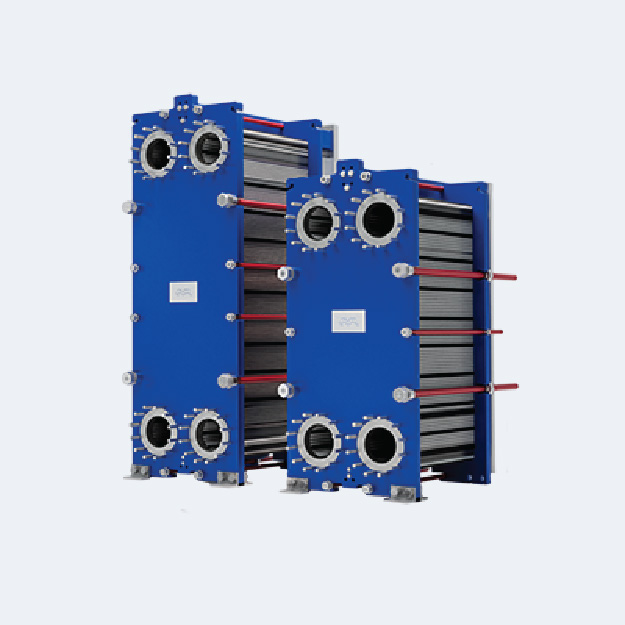
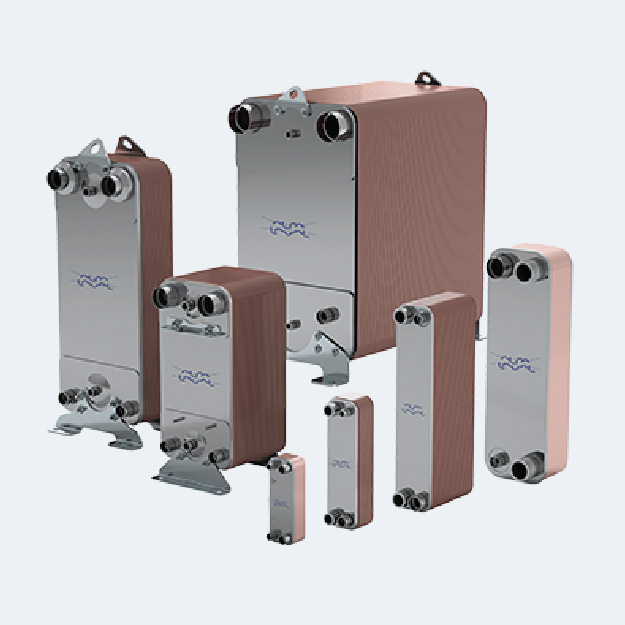
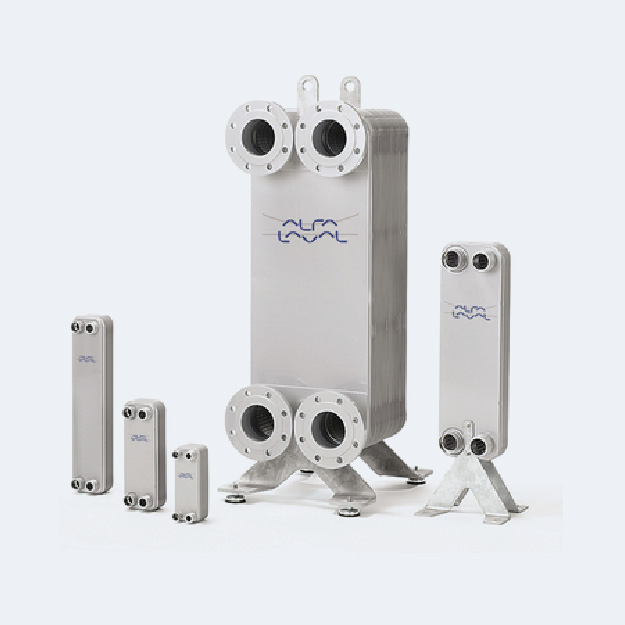
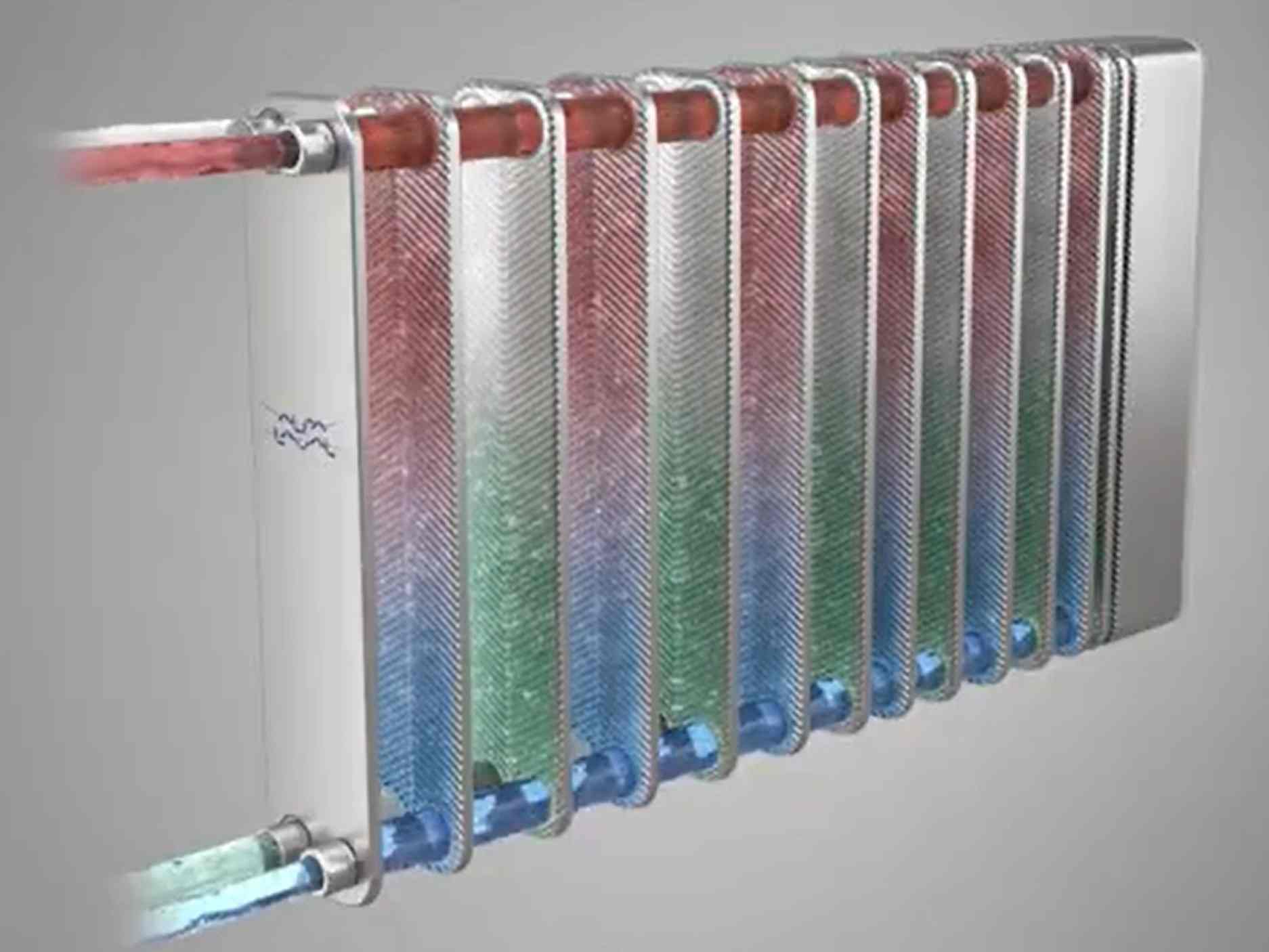
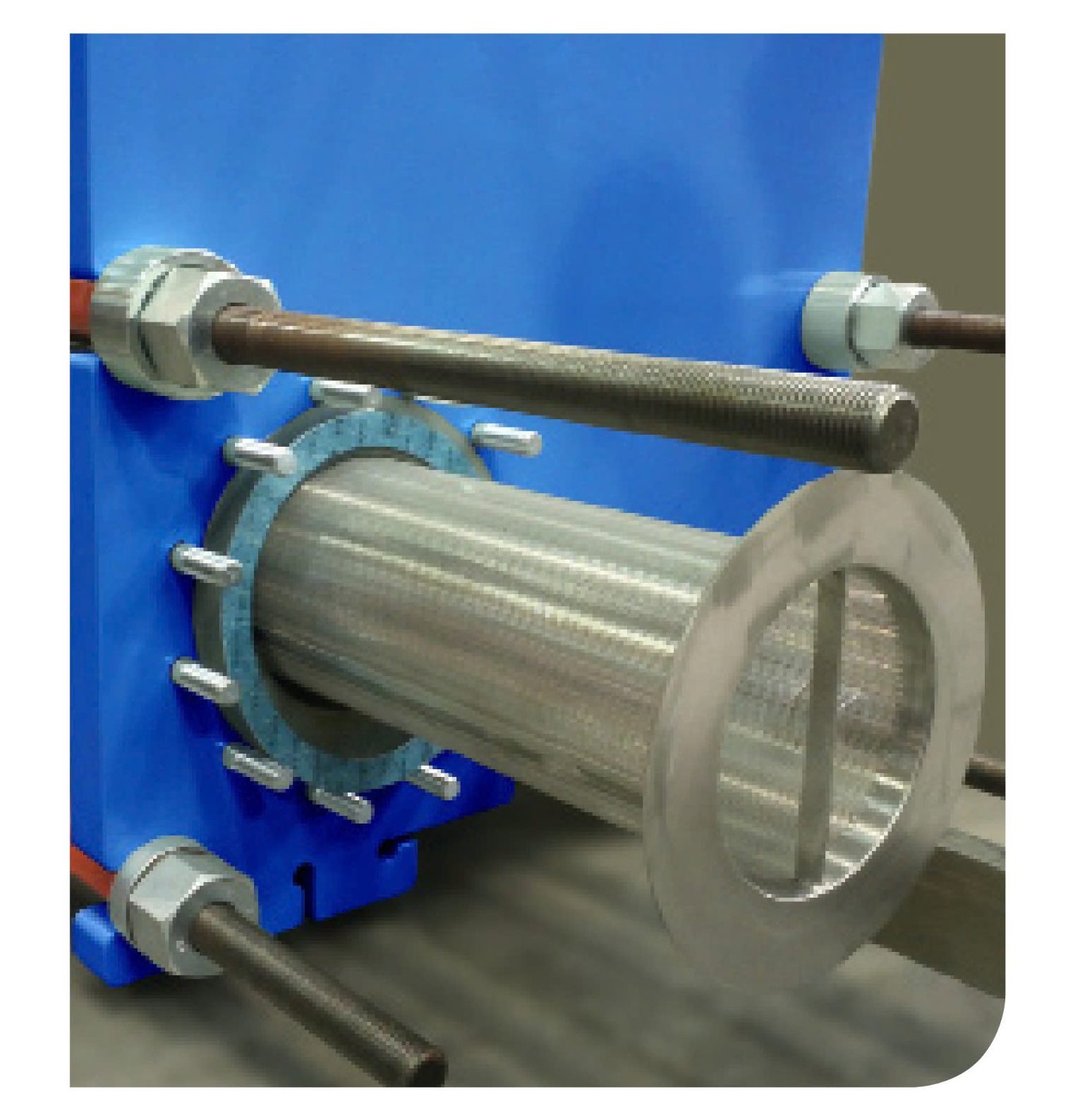
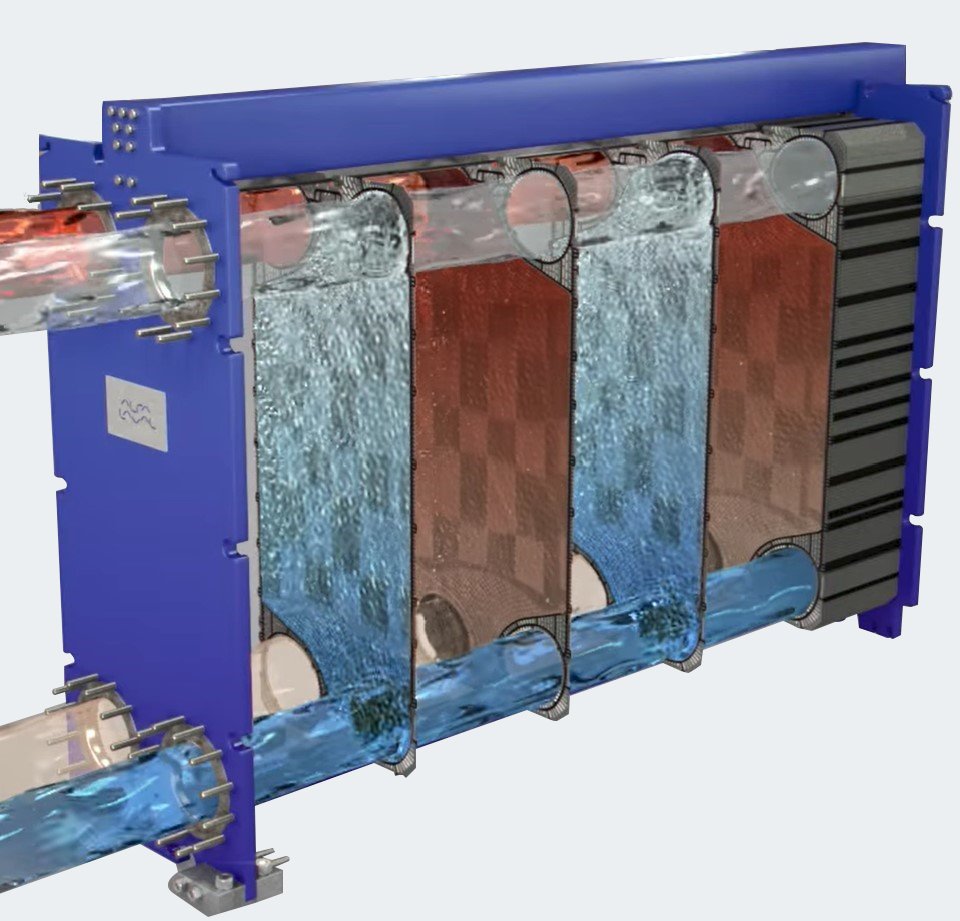
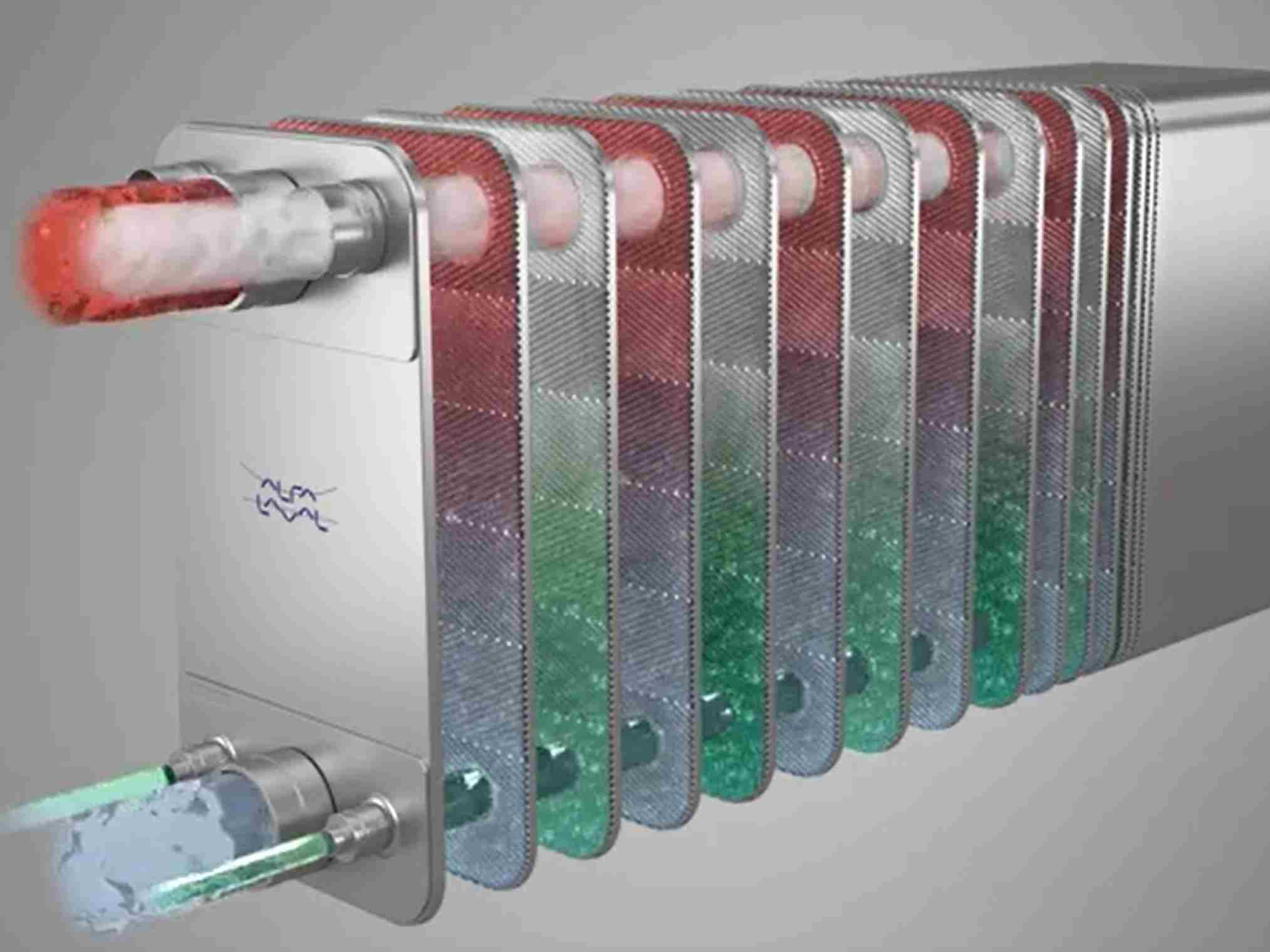
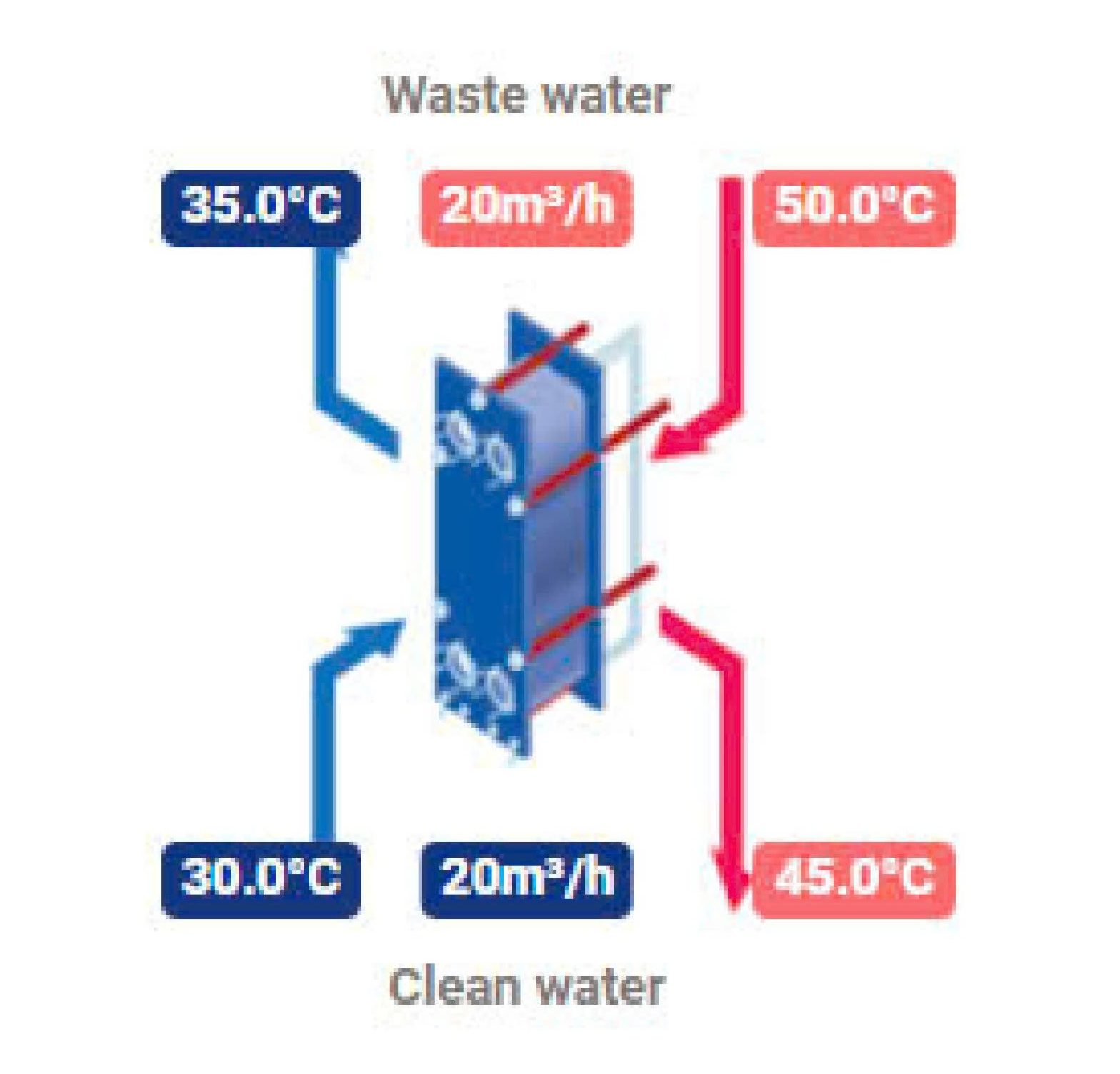
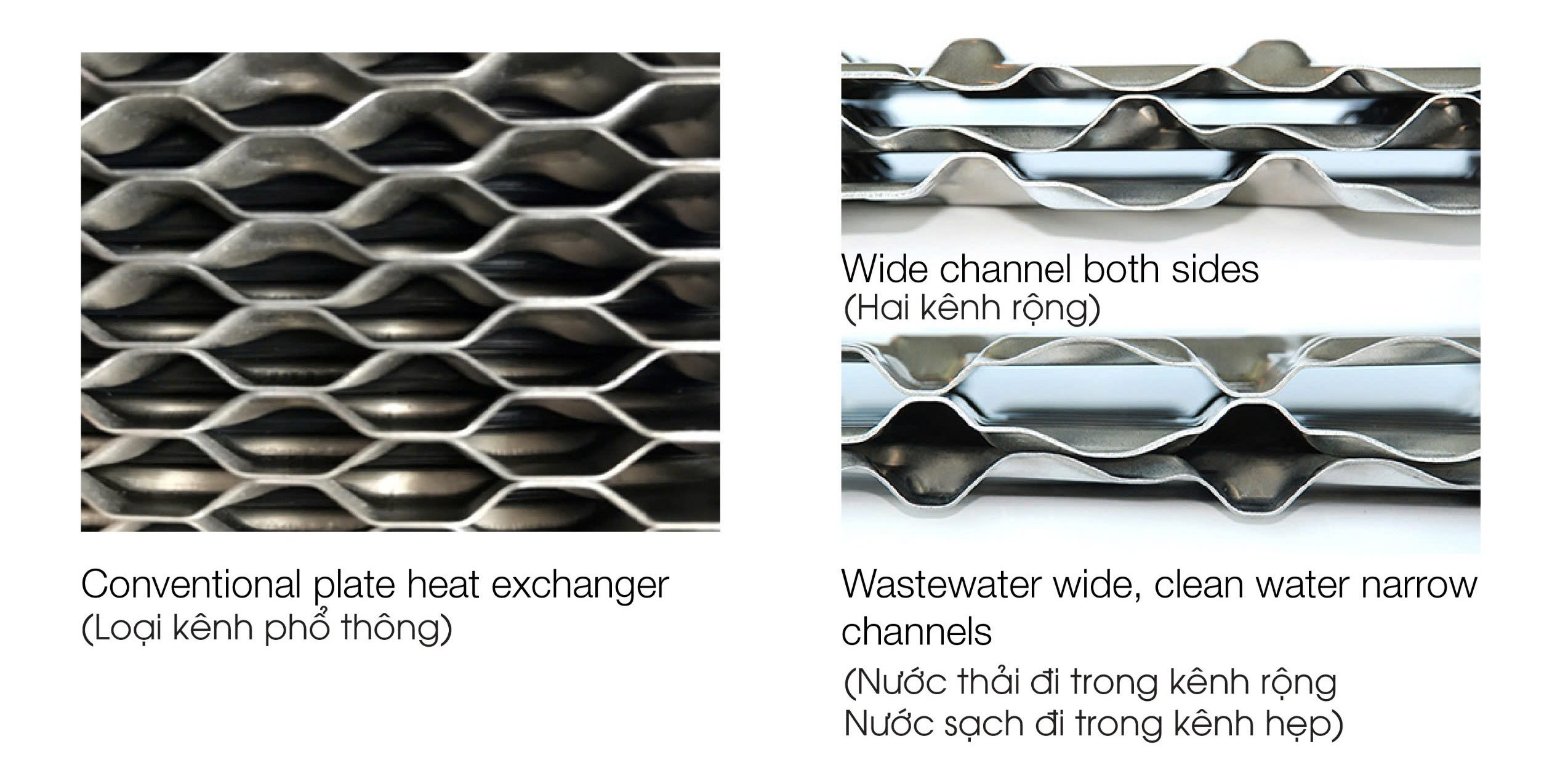
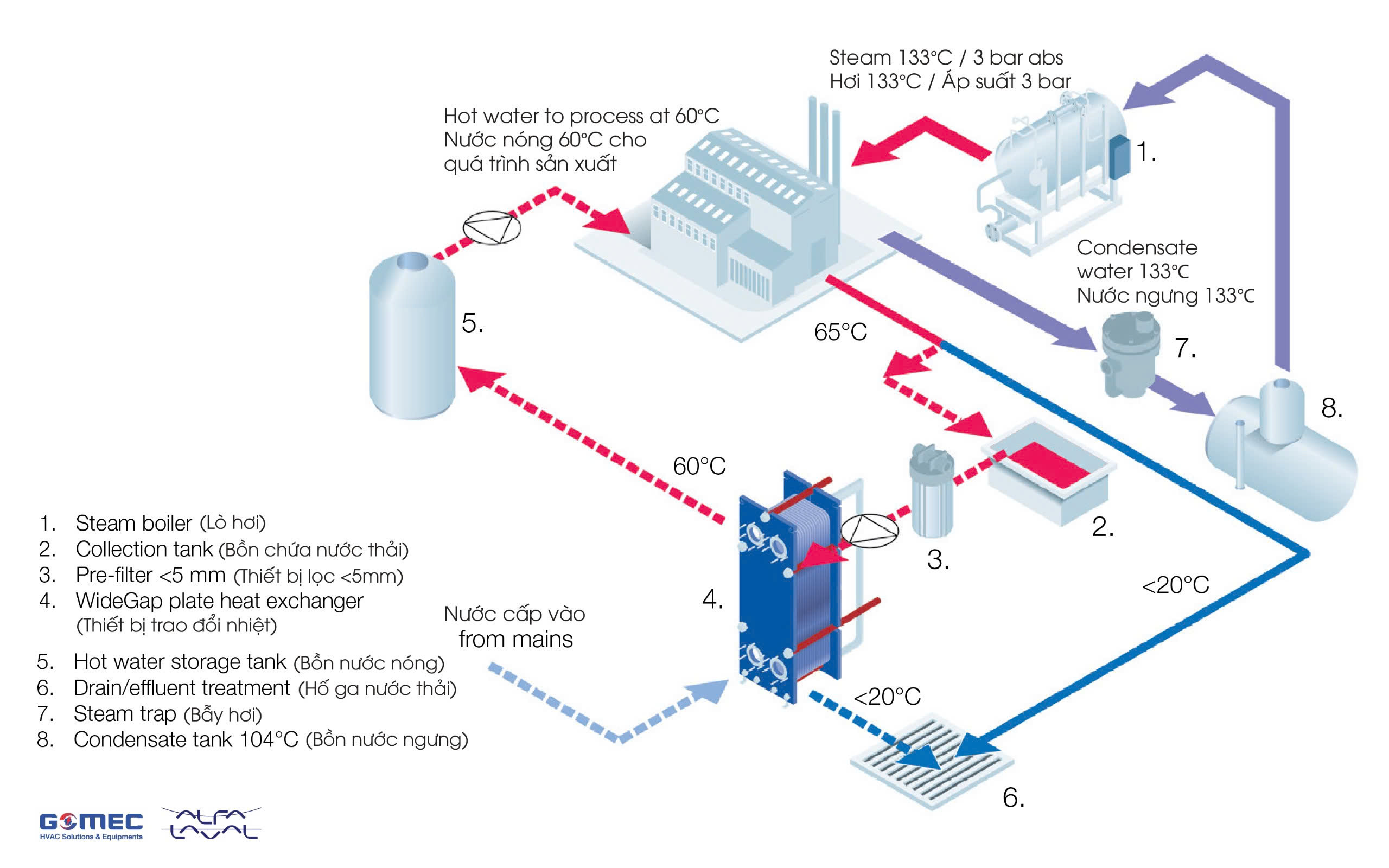
Heat Recovery From Warm Wastewater Solution
Contents/ Mục Lục
Comment
Login
0 Comments
oldest